Part of a series of articles on The mathematical constant, e
Natural logarithm
Applications in Compound interest · Euler's identity & Euler's formula · Half lives & Exponential growth/decay
Defining e Proof that e is irrational · Representations of e · Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem
People John Napier · Leonhard Euler Schanuel's conjecture In mathematical analysis, Euler's identity, named after Leonhard Euler, is the equation
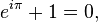
where
 is Euler's number, the base of the natural logarithm,
is Euler's number, the base of the natural logarithm,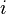 is the imaginary unit, one of the two complex numbers whose square is negative one (the other is
is the imaginary unit, one of the two complex numbers whose square is negative one (the other is  ), and
), and is pi, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
is pi, the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.Euler's identity is also sometimes called Euler's equation.
Nature of the identity
A reader poll conducted by Mathematical Intelligencer named the identity as the most beautiful theorem in mathematics.
Perceptions of the identity
The identity is a special case of Euler's formula from complex analysis, which states that

for any real number x. In particular, if
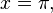
then

Since

and

it follows that

which gives the identity
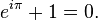
Note that the arguments to the trigonometric functions (sin and cos) are measured in radians.
 Derivation
DerivationEuler's identity is a special case of the more general identity that the n-th roots of unity, for n > 1, add up to 0:

Euler's identity is retrieved from this generalization by putting n = 2.
No comments:
Post a Comment